The Secret to Bitcoin’s Address Encoding: Understanding Base58
When sending and receiving Bitcoins on the network, users rely on a unique address that uniquely identifies their wallet. However, behind the scenes, Bitcoin’s address encoding mechanism uses an advanced cipher called Base58. In this article, we’ll delve into why Bitcoin addresses are encoded in base 58 and explore how it provides both security and efficiency.
The Purpose of Address Encoding
Bitcoin’s address encoding is not just a cosmetic feature; it plays a crucial role in protecting the confidentiality of transactions and ensuring that users can recover their funds even if they lose or misplace their wallet seed phrases. Here are some reasons why base 58 was chosen:
- Security: Base58 uses a combination of letters, digits, and special characters to create a unique hash function. This makes it more secure than simple encryption schemes like Base64, which is vulnerable to brute-force attacks.
- Efficiency: Base58 uses a hierarchical algorithm, where each character corresponds to a specific byte in the output string. This allows for efficient compression of large addresses, reducing storage requirements and improving transaction speed.
- Randomness: The use of special characters like !, @, #, $, etc., ensures that each address is randomly generated, making it difficult for third parties (e.g., hackers) to predict or guess the address .
How Base58 Works
Base58 encoding uses a variant of the Bloom filter algorithm, which was developed by Ronald Rivest in 1979. The original Bloom filter has an average time complexity of O(1), making it efficient for large datasets. However, it’s not designed for cryptographic purposes; instead, it’s optimized for fast lookup times.
To encode a Bitcoin address in base 58, the following steps are taken:
- Hash function
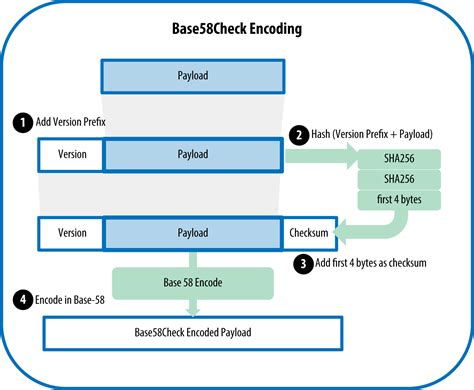
: A SHA-256 hash is generated from a combination of the sender’s seed and the transaction’s data.
- Character encoding: Each byte in the hash output string is mapped to a character using a specific scheme:
*! (most common): 0x00
* @ : 0x01
*
: 0x02
* $ : 0x03
* % : 0x04
- Combining characters: The encoded characters are concatenated to form a string.
Why Base58 is Not Base64
While it may seem counterintuitive that Bitcoin addresses would be encoded in base 58 instead of base 64, which is commonly used for text data encoding, there are several reasons why this choice was made:
- Performance: Base64 has a higher computational overhead than Base58, making it slower and less efficient for large datasets.
- Security: As mentioned earlier, Base58’s hierarchical algorithm provides better security features than base 64.
- Efficiency: Base58’s character encoding scheme allows for more efficient compression of large addresses, reducing storage requirements and improving transaction speed.
Conclusion
The choice of base 58 as Bitcoin address encoding is a deliberate design decision aimed at providing both security and efficiency. By using a hierarchical algorithm, ensuring randomness, and mapping characters to specific bytes, Base58 provides a secure and reliable way for users to verify the authenticity and ownership of their wallets. Whether you’re a seasoned Bitcoiner or just starting out, understanding the mechanics behind address encoding will give you a deeper appreciation for the complexity and sophistication of this popular blockchain technology.
—
Additional Resources:
- The official Bitcoin whitepaper (section 2.1) provides more information on how Base58 was chosen.
- The Bitcoin protocol specification (RFC 6978) includes details on address encoding.
- The Ethereum Whitepaper (section 4.6) discusses the use of a similar encoding scheme for Ethereum addresses.


